A diabetes diet focuses on controlling blood sugar levels by managing carbohydrate intake. It promotes balanced meals and healthy food choices.
Maintaining a nutritious diet is crucial for individuals living with diabetes. By prioritizing a balance of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, they can effectively manage their blood sugar levels and overall health. This diet usually includes plenty of vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and limits sugars and refined carbs.
Portion control and regular meal times form the foundation of the diabetes diet, helping to stabilize blood sugar. The goal is to achieve a diet that supports a healthy weight and heart, while also being rich in nutrients and low in calories and harmful fats. Education from a dietitian can empower those with diabetes to make informed food choices, thus reducing the risk of diabetes-related complications.
Diabetes Diet
A diabetes diet focuses on controlling blood sugar levels through balanced meals. Tailoring your nutrition to include plenty of vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains can lead to better health management.
Diabetes can often feel like a relentless tug-of-war with food choices, but establishing a balanced diet is a cornerstone of managing this condition. The relationship between what you eat and how your body handles blood sugar is direct and complex.
By focusing on a nutritious, tailored diet plan, those living with diabetes can not only keep their glucose levels in check but also improve their overall well-being.
Understanding The Basics Of A Diabetes Diet
Embarking on a diabetes-friendly diet starts with grasping the nutrients that influence blood sugar levels. Carbohydrates have the most significant impact, but fat and protein also play roles. Balance and moderation are key:
- Carbohydrates: Choose complex carbs with a low glycemic index; these digest slower and cause a gradual rise in blood sugar.
- Protein: Lean protein helps maintain muscle mass and doesn’t directly spike blood sugar.
- Fats: Opt for unsaturated fats, which can help maintain heart health.
The Role Of Fiber In A Diabetic Meal Plan
A nutritious places a strong emphasis on fiber because of its dual benefits: it slows digestion, which helps control blood sugar levels, and it promotes satiety, reducing the overall caloric intake. Aim to incorporate a variety of fiber-rich foods such as:
- Legumes: Black beans and lentils are not only high in fiber but also rich in protein.
- Whole Grains: Oats and quinoa offer a hearty dose of fiber without excessive carbohydrate loading.
- Vegetables: Non-starchy varieties like leafy greens and bell peppers provide vitamins and fiber with minimal impact on blood sugar.
Portion Control And Meal Timing
Strategizing when and how much you eat can significantly improve blood glucose control. Frequent, smaller meals or snacks can stave off hunger and prevent blood sugar spikes. Some helpful tips include:
- Using smaller plates to naturally reduce portion sizes without feeling deprived.
- Setting a regular eating schedule to help stabilize blood sugar throughout the day.
The Importance Of Hydration
While food takes center stage in a diabetes diet, hydration shouldn’t be overlooked. Staying well-hydrated is crucial for metabolic processes and can help manage appetite:
- Water: It’s the best option for staying hydrated without adding calories or sugar to your diet.
- Unsweetened Tea: It can be a flavorful alternative to water and may offer antioxidant benefits.
Tailoring Your Diet To Your Lifestyle
Every individual’s lifestyle, tastes, and health status are unique, affecting the specifics of their diabetes diet. Personal preferences and needs should shape your diet plan:
- Activity Level: More active individuals may require a slightly higher intake of carbohydrates for energy.
- Food Allergies or Sensitivities: These can influence food choices, necessitating personalized alternatives to standard recommendations.
Implementing a diabetes diet isn’t just about restrictions—it’s a journey towards understanding and harmony with your body’s needs. The goal is to enjoy a varied, flavorful diet that also aligns with your health goals. With each mindful choice, you’ll be taking a step towards better health and enhanced quality of life.
How To Control Diabetes Diet
Managing a diabetes diet involves choosing foods that regulate blood sugar, like fiber-rich vegetables and whole grains. Opt for lean proteins and monitor carbohydrate intake to maintain steady glucose levels.
Understanding Diabetes And Dietary Control
Managing diabetes effectively involves a careful balance of dietary choices, which contribute significantly to maintaining stable blood glucose levels. Let’s dive into some practical steps you can follow to control your diabetes through diet.
Key Foods To Include In Your Diabetes Diet:
Before outlining the specifics, it’s essential to recognize that a diabetes-friendly diet isn’t just about restrictions; it’s also about ensuring you incorporate nutritious foods that can help regulate your blood sugar. Here are some top choices:
- Non-starchy vegetables: These are high in nutrients and fiber while being low in carbohydrates and calories, making them ideal for blood sugar control.
- Lean proteins: Opt for sources like chicken, fish, and plant-based proteins that have minimal saturated fats.
- Whole grains: They contain more fiber than refined grains, helping to manage blood sugar spikes.
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, and chickpeas are excellent protein sources, also rich in fiber and low on the glycemic index.
- Healthy fats: Foods high in omega-3 fatty acids, such as avocados and nuts, are beneficial for heart health, which is crucial for individuals with diabetes.
Foods To Limit Or Avoid With Diabetes:
When considering what to limit in your diet, remember that certain foods can lead to blood sugar spikes and should generally be consumed in moderation or avoided:
- Sugary drinks: Beverages like soda, sweetened teas, and fruit juices can quickly elevate blood sugar levels.
- Refined carbs: White bread, pasta, and pastries have little nutritional value and can disrupt glucose control.
- Processed snacks: Often high in salt, sugar, and unhealthy fats, these can lead to weight gain and hinder diabetes management.
- Fatty cuts of meat: Saturated fats in these meats can contribute to insulin resistance.
- Trans fats: Found in some fried and baked goods, trans fats can raise bad cholesterol and lower good cholesterol levels.
Planning Your Meals Effectively:
To stay on track with your diabetes diet, proactive meal planning is a strategy you can’t afford to overlook. Organizing your meals ensures you have the right foods on hand when you need them, preventing spontaneous decisions that may not align with your dietary goals.
Strategies To Stay Consistent With Your Diabetes Diet:
Staying consistent might seem daunting, but with the right approach, you can make it a sustainable part of your lifestyle. Here’s how you can keep your diet on track:
- Set realistic goals: Smaller, manageable dietary changes are more sustainable than drastic ones.
- Prepare meals in advance: This can help you resist the temptation of unhealthy convenience foods.
- Monitor your portion sizes: Using measuring tools or a plate method can be effective in controlling portions.
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to help manage hunger and maintain overall health.
- Seek support: Whether from a dietitian, diabetes support group, or friends and family, a support network can greatly assist in your journey.
Embracing a manageable, balanced approach to your diet can lead to better overall health and diabetes control. Remember that every individual is different, and it’s essential to tailor your dietary choices to your specific needs and medical advice. Small, consistent steps can make a significant impact on managing your condition and enhancing your quality of life.
Type 2 Diabetes Diet
Navigating a diabetes diet requires balancing nutritious foods with controlled carb intake. Embrace whole grains, lean proteins, and ample vegetables to manage blood sugar levels effectively.
Managing your diet when you have type 2 diabetes can be challenging, but with the right guidance and knowledge, it’s certainly an achievable goal. A balanced diet is crucial in regulating blood sugar levels, maintaining a healthy weight, and controlling the risk factors associated with diabetes.
Here’s how you can structure your diet to support your health and well-being.
Understanding Carbohydrates In A Type 2 Diabetes Diet
Carbohydrates have a significant impact on blood sugar levels. It is essential to understand which carbs to include and which to limit:
- Complex carbohydrates: These are found in whole grains, legumes, and vegetables. Because they are digested more slowly, they help in maintaining steady blood sugar levels.
- Simple carbohydrates: Generally found in sugary foods and drinks, these carbs are rapidly absorbed, causing quick spikes in blood sugar. It’s best to minimize intake of these.
- Fiber: High-fiber foods not only help regulate blood sugar levels but also promote a healthy digestive system. Aim to include a variety of fiber-rich foods such as fruits, vegetables, and nuts.
The Importance Of Monitoring Glycemic Index
Glycemic Index (GI) is a value used to measure how much specific foods increase blood sugar levels. Consuming low-GI foods is integral for those managing type 2 diabetes:
- Low-GI foods: These cause a gradual rise in blood sugar and include options like whole wheat bread, oatmeal, and non-starchy vegetables.
- High-GI foods: Typically cause a fast increase in blood sugar and include white bread, white rice, and sugary cereals. Limit these to maintain better glucose control.
Including Healthy Fats In Your Diet
Contrary to popular belief, fats are an important part of a diabetes-friendly diet, provided you choose the right kinds:
- Monounsaturated fats: Found in foods like avocados, nuts, and olive oil, these fats can help to improve blood cholesterol levels.
- Polyunsaturated fats: Sources such as fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts are rich in omega-3 fatty acids and contribute to heart health.
- Saturated and trans fats: Often present in processed foods, these can increase the risk of heart disease and should be consumed in moderation.
Protein Choices For Type 2 Diabetes
Protein is a key component of any healthy diet and has a minimal effect on blood glucose levels. It should be included in each meal:
- Plant-based proteins: Beans, lentils, and tofu are excellent, diabetes-friendly protein options.
- Lean animal proteins: Opt for fish, chicken, turkey, and lean cuts of beef and pork to reduce saturated fat intake.
- Dairy: Choose low-fat or fat-free dairy products like milk, cheese, and yogurt to add protein while managing calorie and fat intake.
Eating well with type 2 diabetes doesn’t mean you have to give up your favorite foods. It’s about making smarter food choices, balancing nutrients, and understanding how your body responds to different foods. By following these guidelines, you can take steps towards better managing your diabetes and improving your overall health.
Remember, every step you take on this journey counts. Keep it up!
Diabetes Diet Plan
Managing blood sugar levels is crucial for individuals with diabetes, and a tailored diet plan plays a pivotal role. A nutritious diabetes diet focuses on balancing portion sizes, and incorporating a diverse range of whole foods rich in fiber and low in sugar.
Understanding A Diabetes Diet Plan
Living with diabetes doesn’t mean you have to say goodbye to good food. Actually, a is simply about eating the healthiest foods in moderate amounts and sticking to regular meal times. This plan helps you control your blood sugar (glucose), manage your weight, and control heart disease risk factors, such as high blood pressure and high blood fats.
Foods To Include In Your Diet
Eating right is crucial when managing diabetes. Here’s what should be on your plate:
- Whole Grains: Choose whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat over processed grains. They have more fiber, which helps control blood sugar levels.
- Fruits and Vegetables: These naturals are low in calories and packed with nutrients. Go for fresh, frozen, or canned but watch for added sugars.
- Lean Proteins: Options like chicken, fish, and tofu provide energy without extra fat. Fish rich in omega-3 fatty acids, like salmon, are especially good.
- Legumes: Beans and lentils are excellent protein sources that also offer fiber and other nutrients.
- Healthy Fats: Incorporate avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil in moderation to get beneficial fats.
Foods To Limit Or Avoid
Certain foods can hinder diabetes control. Be mindful of what you should limit:
- Refined Sugars: Sweetened drinks and desserts can cause blood sugar spikes.
- Saturated and Trans Fats: Red meats, deep-fried foods, and baked goods are often high in unhealthy fats.
- High-Sodium Foods: Processed snacks and fast food can increase blood pressure.
- Alcoholic Beverages: Moderation is key, as alcohol can affect blood sugar levels.
Portion Control And Meal Planning
Staying on top of portion sizes is as important as choosing the right foods. Regularly planned meals can help maintain steady blood sugar levels. A registered dietitian can assist you in creating a meal plan tailored to your health goals, food preferences, and lifestyle.
This will likely include carbohydrate counting, especially if you have type 1 diabetes.
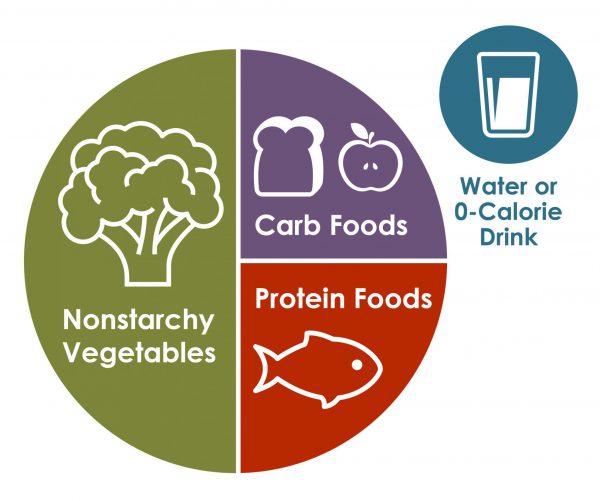
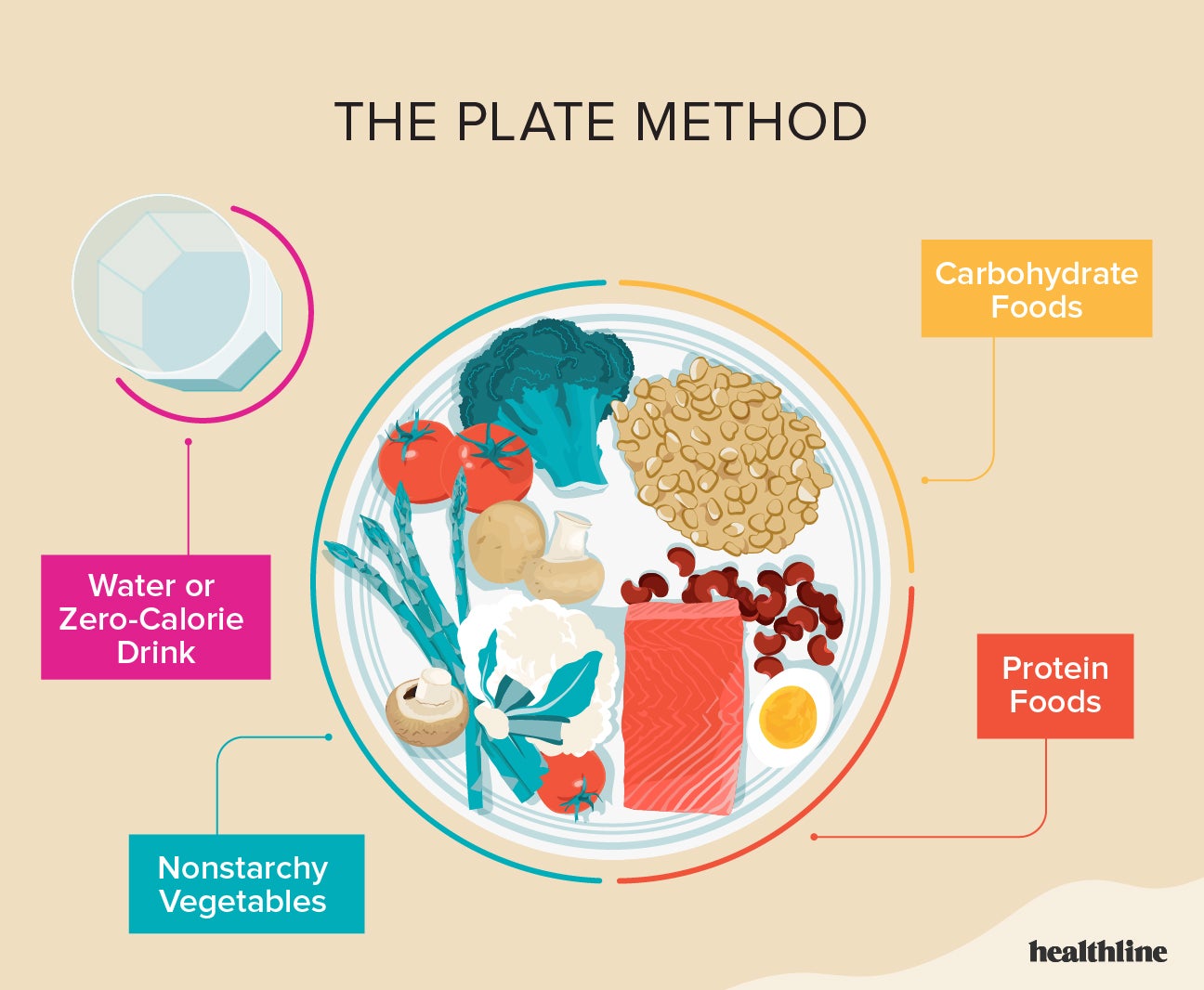
The Plate Method For Easy Meal Planning
Using the plate method simplifies meal planning:
- Half Your Plate: Fill it with non-starchy vegetables like broccoli, spinach, and carrots.
- One Quarter of Your Plate: Should be a lean protein such as chicken, tofu, or fish.
- Remaining Quarter: Reserve for whole grains or starchy vegetables like sweet potatoes.
Staying Hydrated The Right Way
Hydration is crucial, but what you choose to drink can impact your blood sugar levels.
- Water: It’s the best way to stay hydrated without adding calories or sugar.
- Unsweetened Tea: Herbal or black tea can be a good alternative to sugary beverages.
- Coffee: Keep it black or use a sugar substitute if needed.
Remember, a diabetes diet is not a restrictive diet but rather a healthy-eating plan that’s naturally rich in nutrients and low in fat and calories. With the right approach and knowledge, you can enjoy delicious meals while keeping your diabetes under control.
Frequently Asked Questions On Diabetes Diet
What Foods Control Blood Sugar Levels?
Including low glycemic index foods like whole grains, leafy greens, and lean protein can help maintain consistent blood sugar levels.
Can Diabetics Eat Fruit?
Yes, diabetics can enjoy fruit, but they should choose options low in sugar and monitor portion sizes to manage glucose levels.
How Often Should Diabetics Eat?
Diabetics are recommended to eat regular, balanced meals and snacks every 3-4 hours to help regulate blood sugar levels.
Is A High-protein Diet Good For Diabetics?
A high-protein diet can support blood sugar control for diabetics, but it’s vital to choose lean proteins and consider kidney health.
Conclusion
Managing your diabetes through diet is a balancing act, but it’s one you can master. Remember, whole foods and consistent meal timing are your allies. Keep portions in check and carbohydrates consistent. Embrace the power of fiber and hydration. By following these dietary cornerstones, you’re stepping towards a healthier, more vibrant life.
Control your diabetes; don’t let it control you.